📊 What Is Data Sourcing? A Complete Guide to Public & Private Data
In today’s digital age, data is currency. Whether you’re building AI models, driving business intelligence, or optimizing systems, your insights are only as good as your data. That’s where data sourcing comes in—a crucial but often overlooked first step in the data pipeline.
In this blog, we’ll break down:
– What data sourcing is
– Types of data (internal, public, private)
– Methods of data sourcing
– Real-world examples
– Key challenges and best practices
🧾 What is Data Sourcing?
Data sourcing is the process of identifying, acquiring, and collecting data from various sources—internal systems, external APIs, public datasets, or private vendors—for use in decision-making, analytics, or automation. Simply put: Data sourcing is about getting the right data from the right place at the right time.
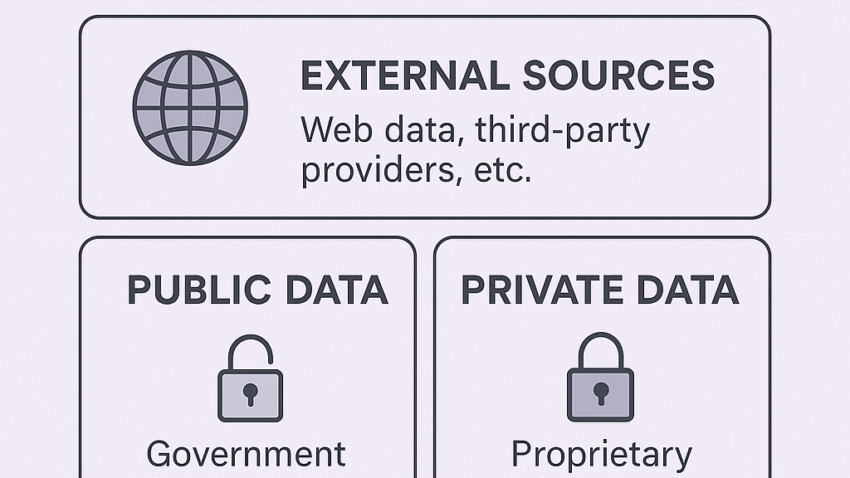
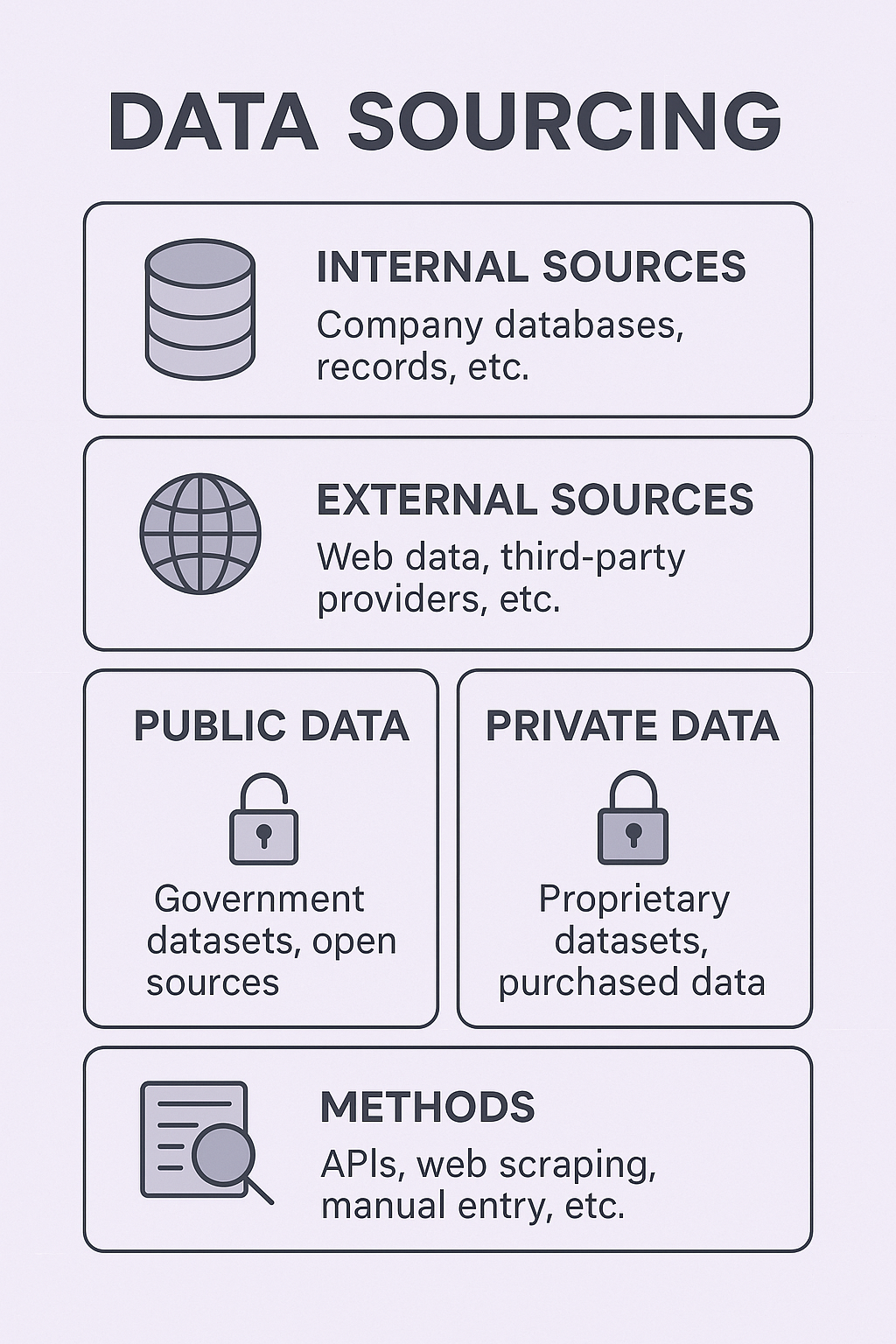
🧩 Types of Data Sources
Data can come from multiple origins. Let’s divide them into major categories:
1. Internal Data
This is data generated within your organization. It is usually proprietary and easily accessible.
Examples:
1. CRM data (e.g., customer interactions)
2. Transaction logs
3. Website analytics
4. IoT sensor outputs
2. External Data
Sourced from outside the organization, external data can be:
🔓 Public Data
Freely accessible and often open for public use.
Examples:
1. Government portals (e.g., data.gov)
2. WHO health statistics
3. OpenStreetMap
4. Public APIs (e.g., weather, traffic)
🔐 Private Data
Proprietary data owned by individuals or organizations, typically requiring licensing, purchase, or agreement.
Examples:
1. Market research from firms like Gartner or Nielsen
2. Social media platform insights
3. Commercial transaction data
4. Customer credit scores from Experience
⚙️ Common Methods of Data Sourcing
Method Description
APIs: Pull data in real-time or scheduled batches.
Web Scraping: Extract data from public websites using scripts.
ETL Pipelines: Extract → Transform → Load structured data into storage or analysis systems.
Manual Entry: Data collected via forms, surveys, or field research.
Data Marketplaces: Buy or license datasets from commercial vendors (e.g., AWS Data Exchange).
⚠️ Challenges in Data Sourcing
While data is abundant, sourcing it isn’t always easy. Common challenges include:
– Data Quality – Incomplete, outdated, or inconsistent data can mislead analysis.
– Privacy & Security – Using private or personal data must comply with laws like GDPR, HIPAA.
– Cost – Premium data from vendors can be expensive.
– Integration – Data comes in various formats; merging it into your systems takes effort.









Pretty! This has been aan extremely wonderful article.
Many thanks for providing this info.